Fossil Plants
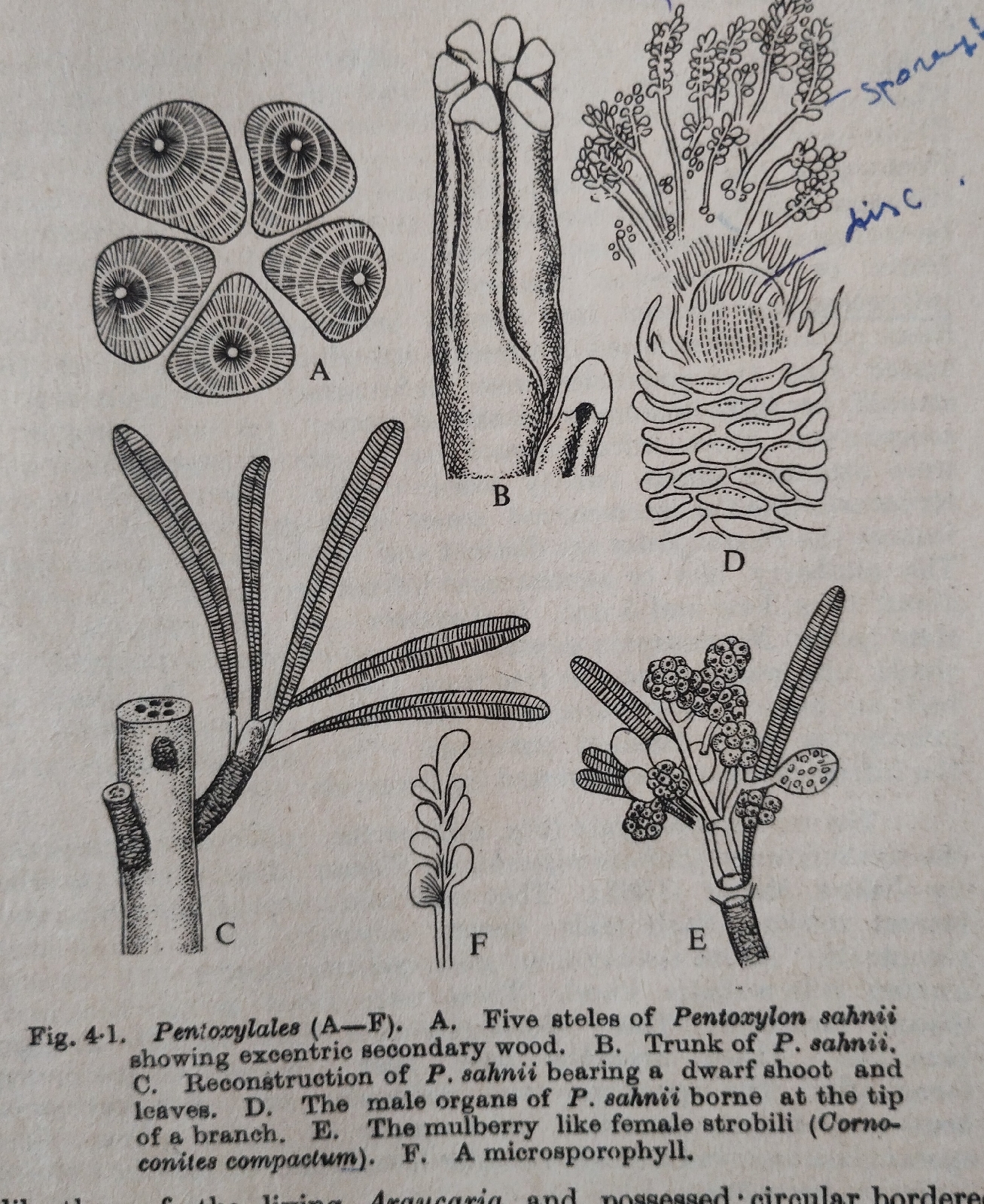
Pentoxylon Fig: A: Female reproductive structures at the apex of pedicles.
Fig: A: Female reproductive structures at the apex of pedicles.
Two stem genera (i) Pentoxylon sahnii and Nepanioxylon were discovered from Rajmahal hills, India.
Morphology:
(1) The stems of P.sahanii were 3 mm to 2 cm in cross section.
(2) Rhomboidal leaf scars were present on the stem.
(3) Leaves were arranged spirally. Leaves were described as Nipaniophyllum raoi.
(4) Leaves simple, petiolate , margin entire, apex obtuse , 7cm long and 1 cm broad with a distinct single mid rib.
(5) Reproductive organs were borne on short lateral shoots.
Stem anatomy:
(1) The stem was polystelic ( with 5 steles).
(2) Each style was concentric with own cambium but in older stem secondary wood turned into excentric.
(3) External to cambium was primary xylem and primary phloem.
(4) Leaf traces were came off from long vascular strands.
(5) There were 5 smaller strands alternating with the 5 main strands.
(6) The secondary xylem was pycnoxylic - it is a coniferous character.
(7) Leaf traces possessed centrifugal and centripetal xylem.
Reproductive structure :
Male reproductive organs:
Male flowers or microsporangiate or pollen bearing organs were described by Vishnu Mitter as Sahnia nipaniensis.
(1) Male flowers borne terminally on short lateral shoots.
(2) A flower had a dome shaped receptacle.
(3) About 24 microsporangiophores were arranged in a single whorl and fused to form a discoid structure.
(4) The sporangia were unilocular with boat shaped and monolete mocrospores or pollen grains .
Female reproductive structures:
B: A seed with Ovule and Integument.
Two species of seed bearing structures were discovered by Sahni and Srivastava from the Jurassic horizon of Rajmahal hills. These were Cornoconites compactum and C. laxum.
(1) The peduncle of the female structure was divided into many pedicles.
(2) Each pedicel terminated in a female strobilus.
(3) The strobili or infructescences measured 1.8 cm long in C. compactum with a central receptacle with about 20 sessile ovules.
(4) There were no sterile structures.
(5) Ovule was surrounded by a single integument which was free from the nucleus.
(6) Integument had outer fleshy sarcotesta and inner stony sclerotesta.
(7) Micropyle directed outwards.
(8) Cone axis was traversed by 5 vascular strands.



Comments
Post a Comment